
This Solution Overview is intended for IT personnel interested in the VMware perspective on the implications for IT of the forthcoming General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) which is due to become enforceable in the European Union from 25th May 2018. Further, we aim to show where the VMware portfolio can help customers to implement solutions for data protection use cases, which in turn, may form part of an organization’s efforts to comply with the GDPR.
The GDPR – What Is It?
The General Data Protection Regulation (Regulation [EU] 2016/679) is a regulation which will strengthen and unify data privacy rights for persons within the European Union (EU).
The GDPR also addresses the export of personal data outside EU borders. Its primary objectives are to give control over personal data – any identifiable information such as name, address, and national identifier numbers – back to the individual as a basic right and to simplify the regulatory environment for international business by harmonising data protection legislation within all
EU countries.
The GDPR extends the scope of current EU data protection law to non-EU organizations who are processing EU personal data The harmonisation of data protection legislation should make it easier for non-EU organizations to comply, but this comes at the potential cost of a strict data protection compliance regime, with severe penalties for non-compliance.
The Intersection of IT and the GDPR
The GDPR is comprised of 99 Articles governing the public policies designed to protect personal data. Only a handful actually relate to IT data protection and cyber-security.
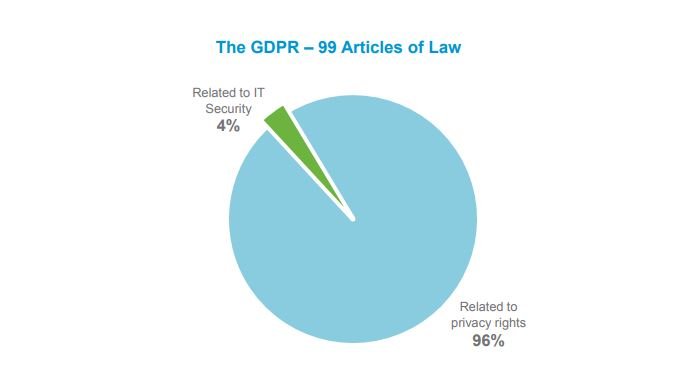
Specific IT data protection solutions have generated a lot of interest in the IT security community because, despite being addressed by only a small number of the 99 Articles, the IT security market overall is exploding. Gartner forecasts €70B in annual global expenditure in 20184 and both cyber-security breaches and applicable legislation continue to trend upwards (including a big increase in fines and penalties under national laws).
Additionally, protecting personal data is just one part of a comprehensive IT data protection strategy. Financial information unrelated to personal data, intellectual property and many other data, while equally important to an organization, are out of scope for GDPR data flow mapping.
How Are Organizations Preparing for the GDPR?
Data Risk Assessment
Consultants, outside advisors and existing internal privacy experts can all play a role in helping organizations to prepare for a personal data flow mapping. The outcome of such a mapping activity helps to clarify the data lifecycle of personal data as it flows through the organization. This kind of lifecycle-based approach helps organizations to document how they process personal data—from when and how the data enters the organization—throughout the data “life” to when it is deleted or destroyed. For example, when a customer fills out a web form to learn more about a service that the organization offers, they will enter their name and contact information. The path of that record can be followed and documented throughout the organization to understand who has access to it and how it is protected. The four key questions organizations need to answer, before being able to assess risk and GDPR readiness are as follows:
Step One: A data inventory involves both a business processes analyst and a trusted advisor, who together can determine what personal data exists in an organization.
Step Two: Personal data is mapped throughout the data lifecycle, from how and where data is collected to when it is deleted or destroyed. This effort typically involves all the functional groups interacting with that data throughout its lifecycle.
Step Three: Identifies the technologies, processes and people that an organization currently uses to protect personal data.
Step Four: Involves the assignment of accountability to the groups responsible across the business or IT service such as payroll processing or HR.
The business then documents gaps and shortfalls, analyzes risk and creates a remediation plan where necessary. This process can then help to provide a clear-status on organizational readiness for the GDPR and will inform IT.
While the data mapping audit process will be similar for all organizations, the path to readiness for the GDPR varies as each organization’s processes are unique to them. Consequently, each journey to GDPR readiness differs. For a deeper look at a business-wide readiness plan, please view the documentation coming from the national agencies within the EU responsible for GDPR governance.
How Can GDPR Preparation Be Made Proactive
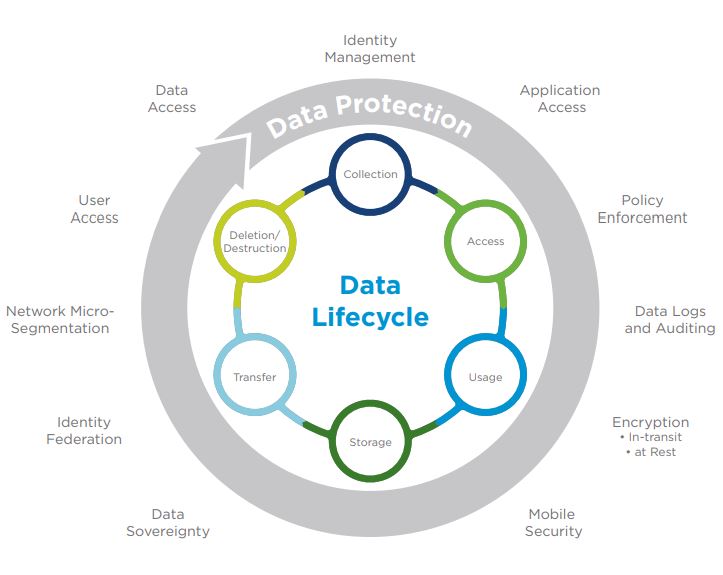
IT can begin preparation by mapping data security use-cases to the data lifecycle. Using a basic data lifecycle as illustrated data below, IT can map any personal data from the first stage, collection, through the final stage, deletion, then identify existing security measures and potential improvements.
Using data access as an example, IT can explore access control, identity management, application access and network access. Examples of questions to explore around personal data as follows:
- Which users have access to what data?
- How is data accessed on mobile devices?
- What types of data can cross which networks?
- Can IT protect the access and usage of personal data from the data center to the end user?
A Transformative IT Approach to Security
The old approach to security was to bolt on a point solution for each security gap. Today, we are at the point of diminishing returns. More spend no longer equates to more security and too much complexity eventually leads to rigidity in IT at a time
when agility is required.
ScholarBuys and VMware can help to provide ubiquitous security from the hybrid cloud to the end user, and across the data lifecycle. We do this by embedding security into the hypervisor and extending that through to the end-user, reducing the complexity of managing IT security.
This approach gives you a powerful platform on which to build, run or manage any application, anywhere and for creating a more secure environment on which you can create competitive dissonance while staying in compliance.


